Galaxy Models
Contents
11. Galaxy Models¶
11.1. Overview¶
Processes
Gravity
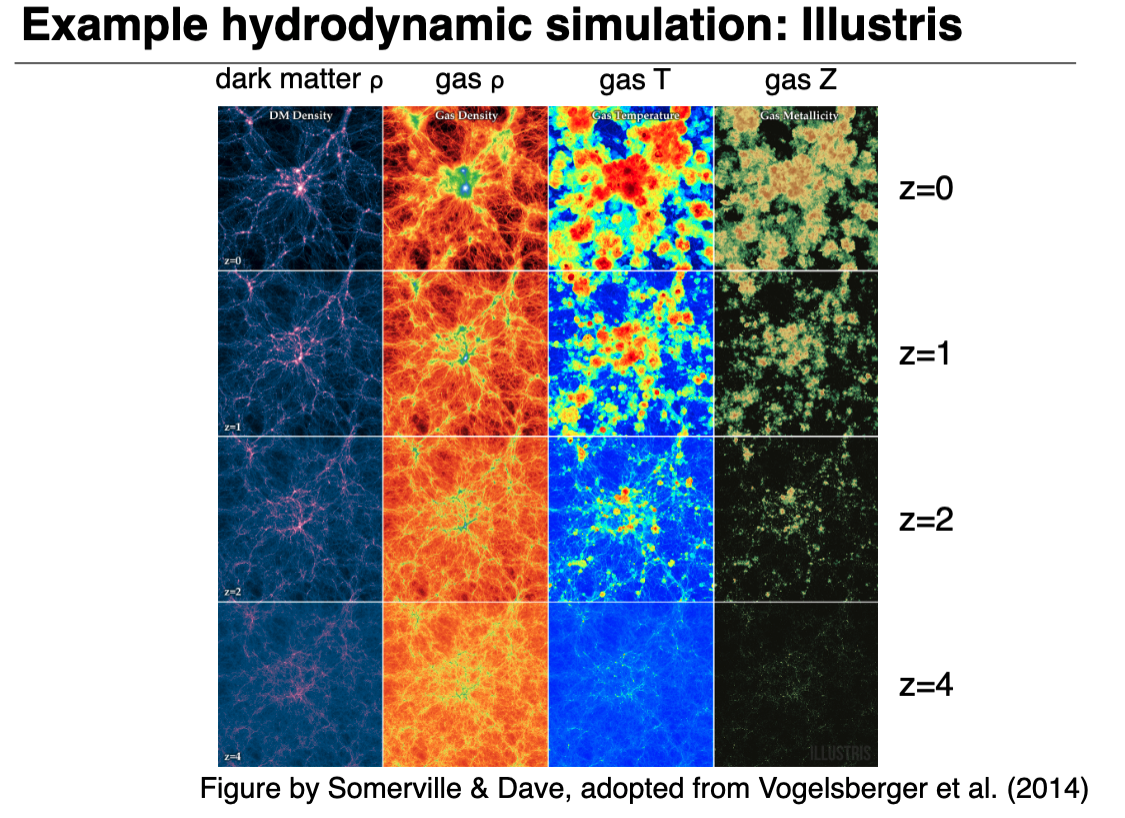
Hydrodynamics
Star formation
BH formation
Star formation feedback
AGN Feedback
Stellar populations and chemical evolutioon
Radiative Transfer
Challenges
Dynamic ranges are huge: \(\sim\) 1 pc scales to \(\sim\) 10 Mpc scales
Time: Age of Universe to dynamical times of galaxies (\(10^6\) years)
Coupling of scales problem – large scales provide the boundary conditions with feedback from small scales affect the large scales
Low Redshift Boundary Conditions: simulations must satisfy these to be good:
Color-magntiude relation of galaxies
Tully-Fisher relation
Luminosity and mass functions
Number of central and satellite galaxies
Mass-metallicty relation
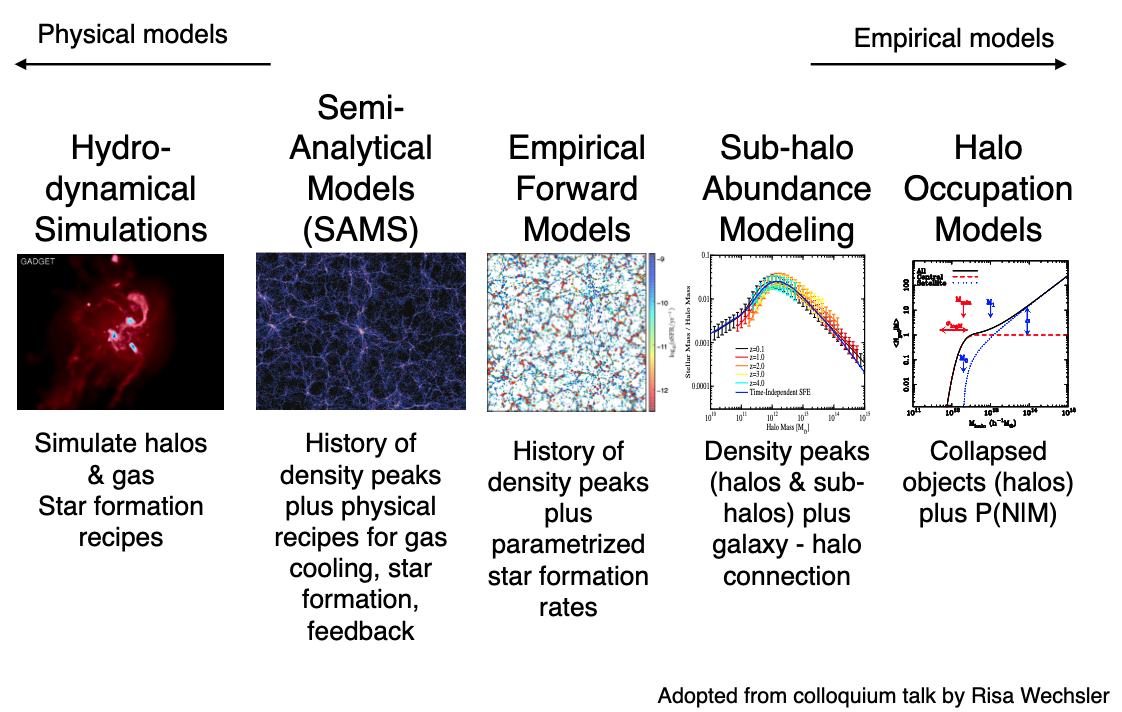
11.2. Semi-Analytic Modeling¶
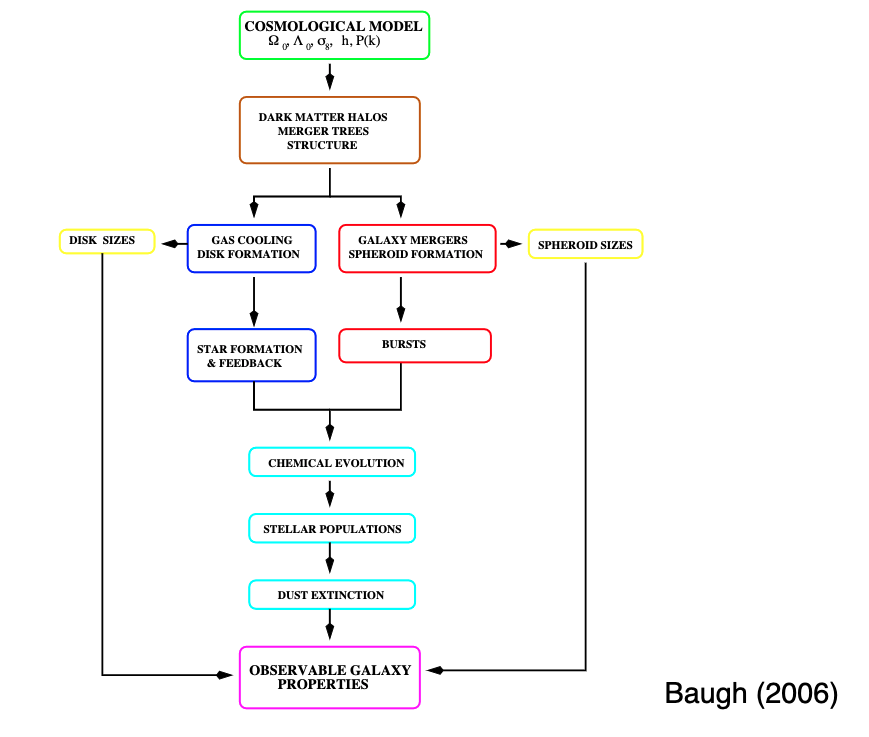
Idea:
WMAP cosmology, grow structure with n-body sims or Press-Schechter formalism
Put baryons back in using analytic prescriptions or recipes
Recipes:
Cold gas –> Stars (Kennicutt-Schmidt)
Cold gas –> Hot gas by SN feedback
Hot gas –> cool gas by cooling via atomic line transitions (depends on density, temperature, and metallicity)
Prescription for how the gas cools (and how much angular momentum it retains)
Evolution of stellar populations and chemical abundances
Mergers of galaxies within the dark matter haloes
Allow free parameters like SF efficiency, stellar feedback efficiency, etc
Repeat this procedure for a large number of \(z=0\) haloes that properly sample the present-day halo mass function
Challenges of SAMS
Too many massive galaxies
Massive galaxies are too blue
Too many low mass galaxies
Tully-Fisher zero point is not matched, galaxies spin too fast
Does not match luminosity function at high \(z>2\)
11.4. Comparison to Data¶
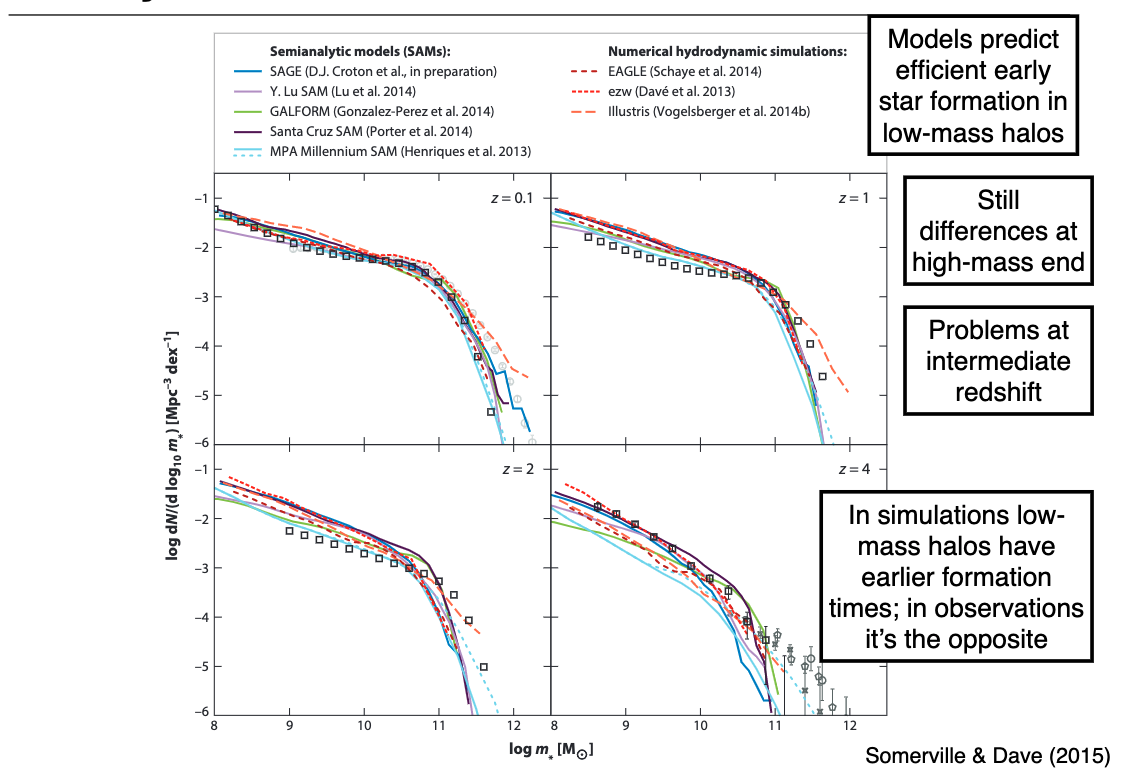
11.4.1. Galaxy Stellar Mass Function¶
Models predict efficient star formation early in low mass halos
Low \(z\) does well though!
Still differences at high mass end
Problems at intermediate redshift
Simulations have low mass haloes forming first; observations show the opposite
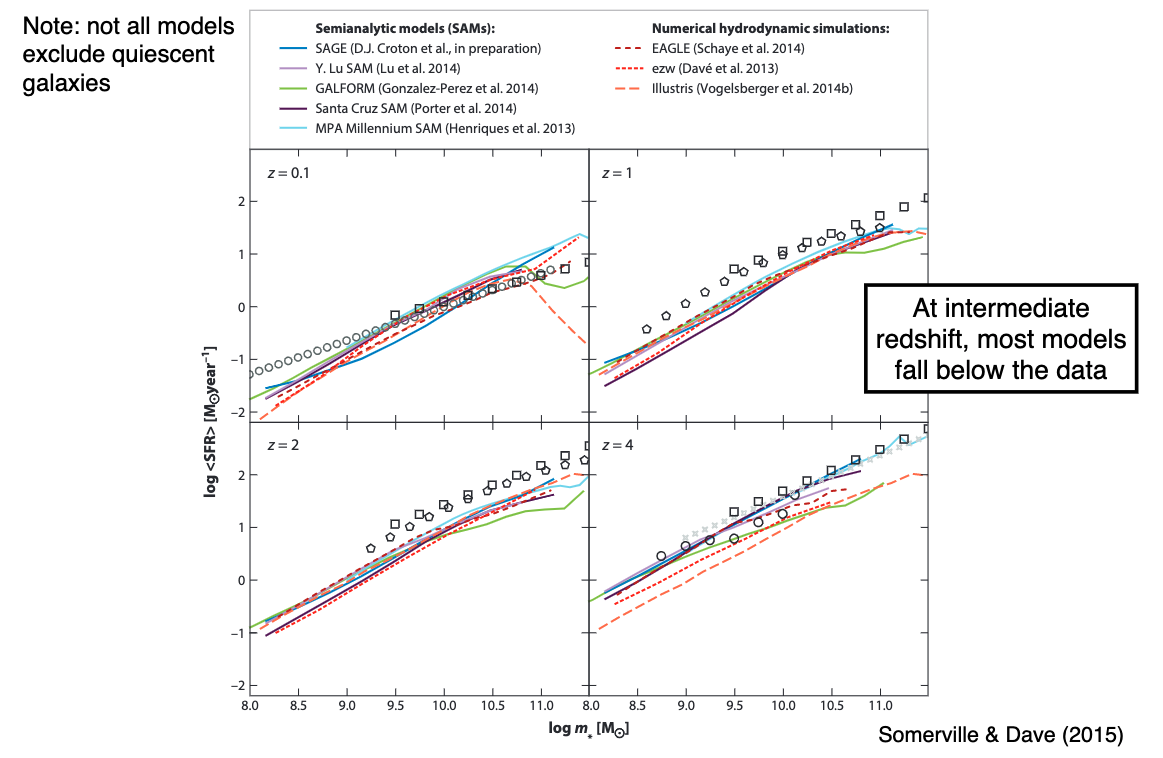
11.4.2. Star Forming Main Sequence¶
A little more discrepant here. Models underpredict data systematically.
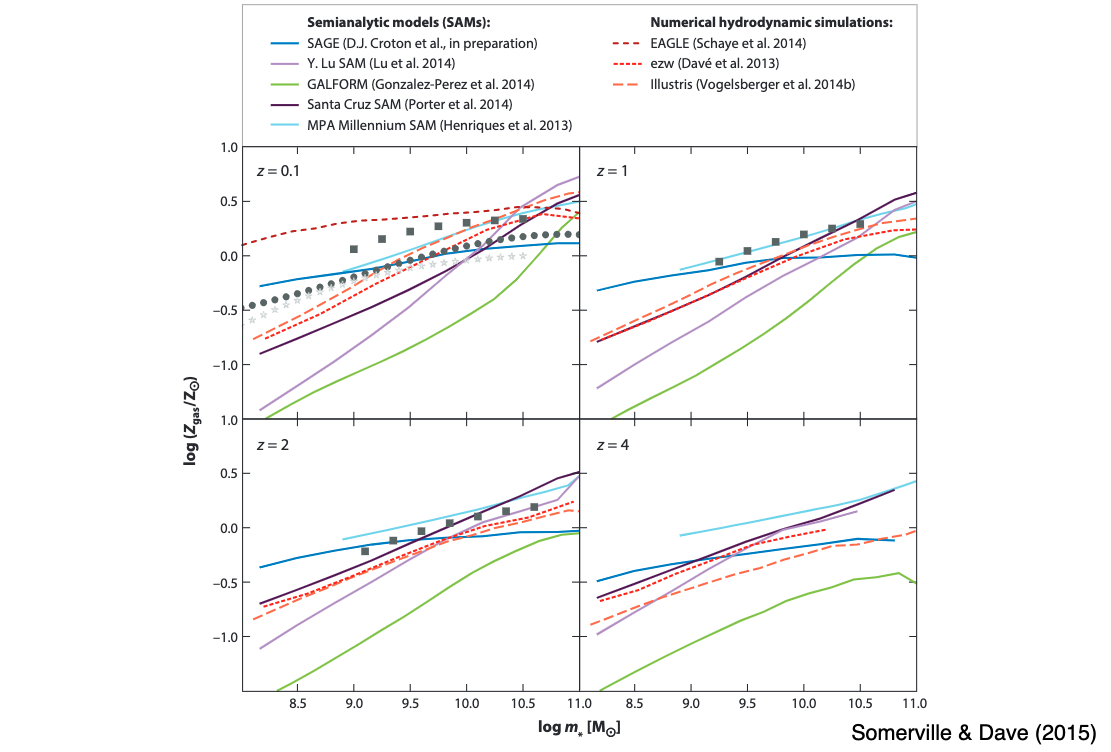
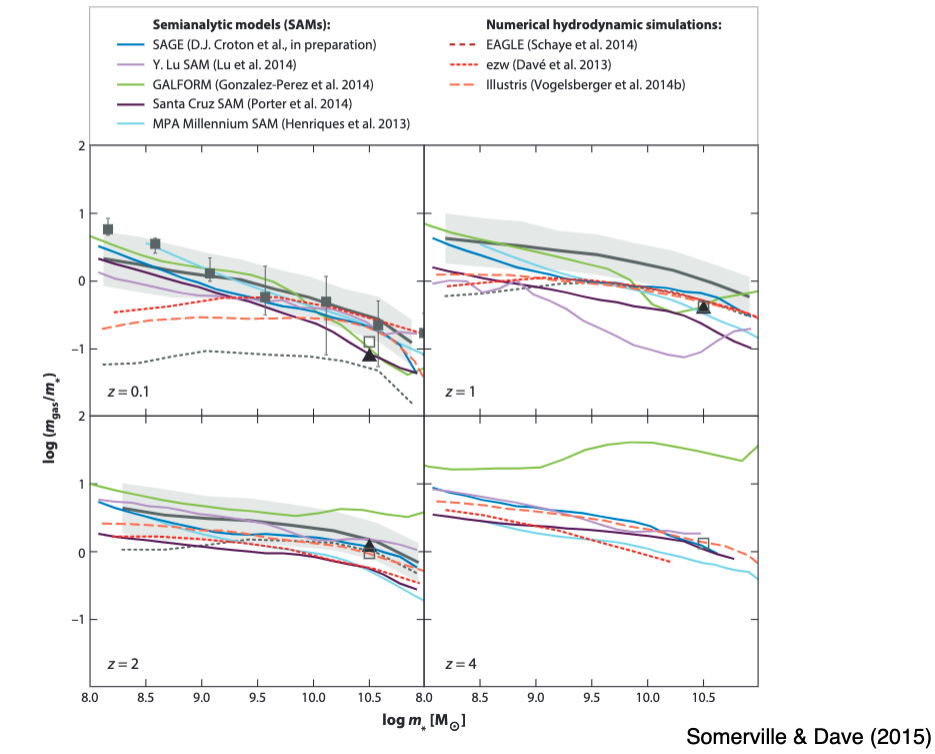
11.4.3. Mass-Metallicity Relation¶