Research
I study the motions of stars in some of the most massive galaxies in the Universe, with the goal of understanding the links between the dynamical structure of a galaxy and its evolution. By simulating many thousands of galaxies, I can fit galaxy simulations to real, high-precision spectroscopic and photometric data to deconstruct a galaxy into its various components: the stars, the dark matter, and the supermassive black hole at the center.
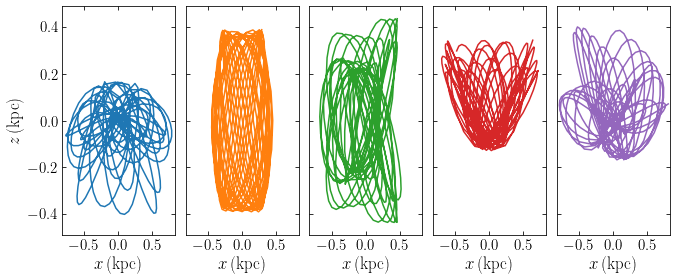 Some stars moving around in a triaxial potential. From Dynamics and Astrophysics of Galaxies, Jo Bovy.
Some stars moving around in a triaxial potential. From Dynamics and Astrophysics of Galaxies, Jo Bovy.
Before I got started on the dynamical modeling of galaxies, I studied novel methods of dark matter detection with Cosmin Ilie at Colgate University. The first stars in the Universe (Population III stars) can accrete dark matter into their center via capture. Self-annihilating dark matter which is accreted provides an additional heating source for Pop. III stars with observational signatures. We worked on showing that the detection of a single Pop. III star can directly constrain the dark matter-nucleon cross section at a level competitive with the best direct detection experiments on the ground. In the best case, our method was able to probe below the Xenon neutrino floor.
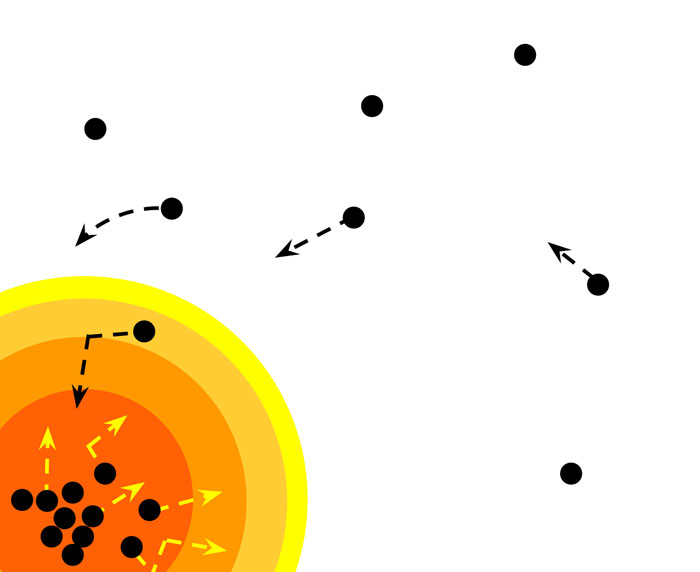 Dark matter being accreted into a star, from here.
Dark matter being accreted into a star, from here.
Outside the realm of astrophysics, I have spent time in the Photonics department at The Aerospace Corporation, a federally funded research and development center (FFRDC). I simulated optical computing implementations of physical neural networks and implemented working optical reservoir computers for classification tasks in the lab.
Publications
2021
-
The MASSIVE Survey - XVII. A Triaxial Orbit-based Determination of the Black Hole Mass and Intrinsic Shape of Elliptical Galaxy NGC 2693, J. D. Pilawa, C. M. Liepold, S. C. Delgado Andrade, J. L. Walsh, C.-P. Ma, M. E. Quenneville, J. E. Greene, J. P. Blakeslee, submitted to ApJ
-
Probing below the neutrino floor with the first generation of stars, C Ilie, C Levy, J Pilawa, S Zhang, arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.11478, submitted to PRD
-
Constraining Dark Matter properties with the first generation of stars, C Ilie, C Levy, J Pilawa, S Zhang arXiv preprint arXiv:2009.11474, submitted to PRL
-
Photonic reservoir computer using speckle in multimode waveguide ring resonators, MN Ashner, U Paudel, M Luengo-Kovac, J Pilawa, GC Valley, Optics Express 29 (13), 19262-19277
2020
-
Comment on “Multiscatter stellar capture of dark matter”, C Ilie, J Pilawa, S Zhang, Physical Review D 102 (4), 048301
-
Radial Star Formation Histories in 32 Nearby Galaxies, DA Dale, KR Anderson, LM Bran, IS Cox, CL Drake, NJ Lee, J Pilawa, …, The Astronomical Journal 159 (5), 195
-
Classification of time-domain waveforms using a speckle-based optical reservoir computer, U Paudel, M Luengo-Kovac, J Pilawa, TJ Shaw, GC Valley, Optics express 28 (2), 1225-1237
